The Tool
EPICO19 is a web application designed to support technicians and decision makers in the Public Health sector for the prediction of the pandemic in progress for the definition of the most effective restrictive measures for containing the infection.
The Pilot phase of EPICO19 officially began in June 2021: the application is tested in the field by the Reggio Emilia AUSL. Health and environmental data are updated on a weekly basis directly on the web application, the analysis report of the last 7 days is generated and the forecast in terms of cases and hospitalizations related to COVID-19 is evaluated for the following week. The project team strongly believes in the EPICO19 application and is employing significant resources to promote it and make it known to new possible users. In order to show the potential of the tool, a free demo version of the application is currently available: to obtain the credentials, send an email to epico19@terraria.com!
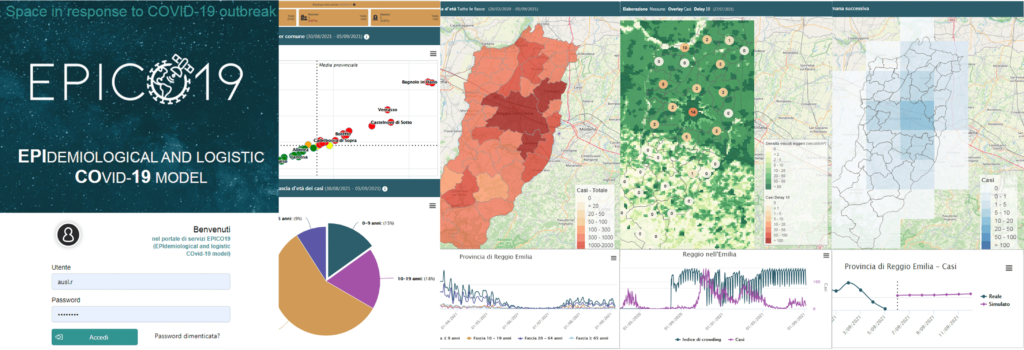
EPICO19 application is a DSS (Decision Support System) that integrates the following features into a single web platform:
- map, monitor and predict the spread of the epidemic through a Machine Learning model
- evaluate the effect of public health policies according to a what-if approach both in the past and in the future: eg. model what would have happened in the first and second wave by identifying the best interventions to better control a possible third wave
- monitor the vulnerability and crowding of the population through satellite observation, respectively by modeling exposure to air pollution and the counting and geolocation of vehicles with an AI engine
Scientifically Based
- "Lockdown timing and efficacy in controlling COVID-19 using mobile phone tracking", EClinicalMedicine 2020, 100457, DOI: 10.1016 / j.eclinm.2020.100457; authors: Marco Vinceti (1,2), Tommaso Filippini (1), Kenneth J. Rothman (2,3), Fabrizio Ferrari (4), Alessia Goffi (4), Giuseppe Maffeis (4), Nicola Orsini (5)
Read the article on Research Gate - "Associations between mortality from COVID-19 in two Italian regions and outdoor air pollution as assessed through tropospheric nitrogen dioxide", November 2020, Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016 / j.scitotenv.2020.143355, authors: Marco Vinceti (1, 2), Tommaso Filippini (1), Kenneth J. Rothman (2,3) Silvia Cocchio (6), [...], Fabrizio Ferrari (4), Alessia Goffi (4)
Read the article on Research Gate - “Satellite-detected tropospheric nitrogen dioxide and spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Northern Italy”, June 2020, Science of The Total Environment; authors: Marco Vinceti (1,2), Tommaso Filippini (1), Kenneth J. Rothman (2,3), [...], Fabrizio Ferrari (4), Alessia Goffi (4)
Read the article on Research Gate
Planning support
The key users to which EPICO19 is addressed are first of all the Local Health Authorities but more generally the public bodies that have responsibility in the management of epidemics, including Municipalities, Provinces and Regions.
The EPICO19 system will be tested during the pilot phase in the province of Reggio Emilia, unfortunately hit very hard by COVID-19 in the first wave, thanks to the user “Azienda USL of Reggio Emilia” directly involved in the project right from the drafting. Reggio Emilia AUSL acts on 42 Municipalities, 7 Municipalities Union for 535'000 inhabitants and 6 Hospitals dealing with the management of health and epidemic policies.
Advanced technological resources
To estimate the crowding index, satellite and aerial VHR images are used, with a ground resolution of 30-50 cm and 11 cm respectively. The images will be analysed by Studiomapp's proprietary Artificial Intelligence vision algorithm, extracting up to 100 classes of objects. This allows you to count the number of cars, buses or trucks and to assess the presence of people at sites where crowding is expected, such as hospitals, parking lots, supermarkets, workplaces, train stations and logistics hubs.
Air pollution and the crowding index are among the inputs of the epidemiological model within the EPICO19 tool. EPICO19 therefore combines advanced artificial intelligence and environmental techniques based on satellite resources with machine learning techniques on epidemiological data.
We take advantage of the CAMS analysis service (a compromise between prediction and reanalysis) which incorporates observations from satellite instruments (for example Sentinel-5P) and ground data, combining them with modeling to estimate the concentration of PM10, PM2.5, NO2 in the air. Air pollution is used to assess the vulnerability of the population and the weather conditions that can influence the spread of the infection.
Scientifically Based
The methodological background behind EPICO19 lies in the following scientific articles:- “Lockdown timing and efficacy in controlling COVID-19 using mobile phone tracking”, EClinicalMedicine 2020, 100457, DOI: 10.1016 / j.eclinm.2020.100457; authors: Marco Vinceti (1,2), Tommaso Filippini (1), Kenneth J. Rothman (2,3), Fabrizio Ferrari (4), Alessia Goffi (4), Giuseppe Maffeis (4), Nicola Orsini (5) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342890867_Lockdown_timing_and_efficacy_in_controlling_COVID-19_using_mobile_phone_tracking
- “Associations between mortality from COVID-19 in two Italian regions and outdoor air pollution as assessed through tropospheric nitrogen dioxide”, November 2020, Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016 / j.scitotenv.2020.143355, authors: Marco Vinceti (1, 2), Tommaso Filippini (1), Kenneth J. Rothman (2,3) Silvia Cocchio (6), […], Fabrizio Ferrari (4), Alessia Goffi (4) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/345725051_Associations_between_mortality_from_COVID-19_in_two_Italian_regions_and_outdoor_air_pollution_as_assessed_through_tropospheric_nitrogen_dioxide
- “Satellite-detected tropospheric nitrogen dioxide and spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Northern Italy”, June 2020, Science of The Total Environment; authors: Marco Vinceti (1,2), Tommaso Filippini (1), Kenneth J. Rothman (2,3), […], Fabrizio Ferrari (4), Alessia Goffi (4) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342203048_Satellite-detected_tropospheric_nitrogen_dioxide_and_spread_of_SARS-CoV-2_infection_in_Northern_Italy
Planning support
The key users to which EPICO19 is addressed are first of all the Local Health Authorities but more generally the public bodies that have responsibility in the management of epidemics, including Municipalities, Provinces and Regions.
The EPICO19 system will be tested during the pilot phase in the province of Reggio Emilia, unfortunately hit very hard by COVID-19 in the first wave, thanks to the user “Azienda USL of Reggio Emilia” directly involved in the project right from the drafting. Reggio Emilia AUSL acts on 42 Municipalities, 7 Municipalities Union for 535’000 inhabitants and 6 Hospitals dealing with the management of health and epidemic policies.
Advanced technological resources
To estimate the crowding index, satellite and aerial VHR images are used, with a ground resolution of 30-50 cm and 11 cm respectively. The images will be analysed by Studiomapp’s proprietary Artificial Intelligence vision algorithm, extracting up to 100 classes of objects. This allows you to count the number of cars, buses or trucks and to assess the presence of people at sites where crowding is expected, such as hospitals, parking lots, supermarkets, workplaces, train stations and logistics hubs.
Air pollution and the crowding index are among the inputs of the epidemiological model within the EPICO19 tool. EPICO19 therefore combines advanced artificial intelligence and environmental techniques based on satellite resources with machine learning techniques on epidemiological data.
We take advantage of the CAMS analysis service (a compromise between prediction and reanalysis) which incorporates observations from satellite instruments (for example Sentinel-5P) and ground data, combining them with modeling to estimate the concentration of PM10, PM2.5, NO2 in the air. Air pollution is used to assess the vulnerability of the population and the weather conditions that can influence the spread of the infection.
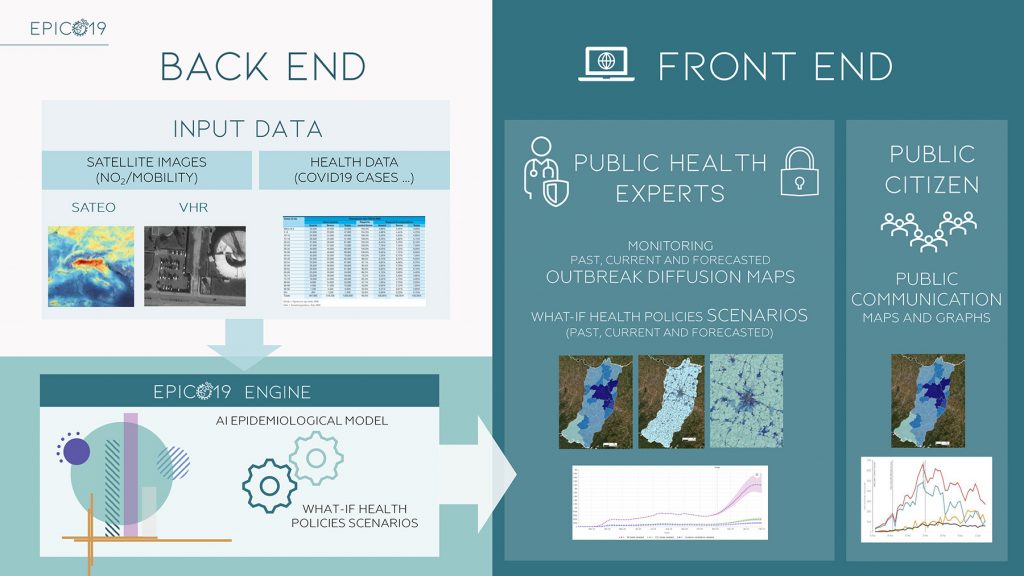
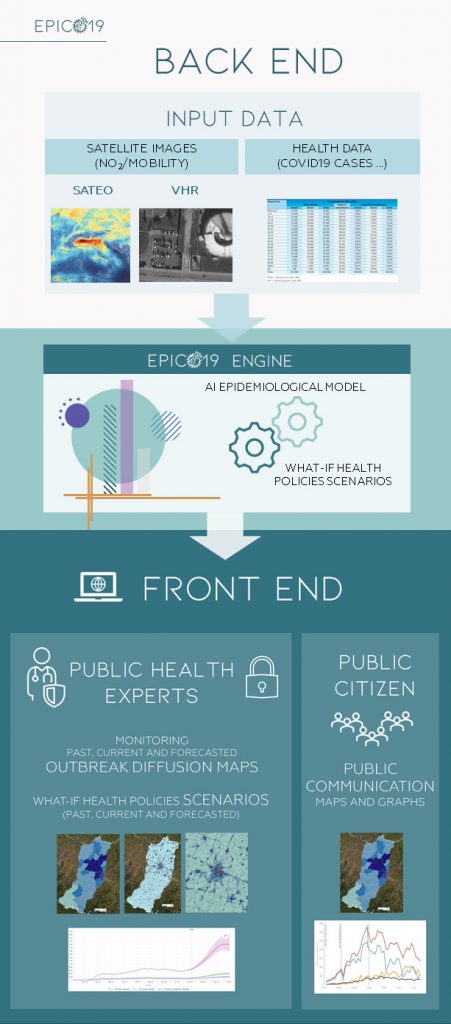
The EPICO19 system consists of:
Back-End (BE)
The set of processes, DBs and pre/post processors that make up the “engine” of the system. Its main components are:
- Spatial and temporal database of health parameters
- Environmental parameters database obtained from satellite images (crowding and concentrations of NO2 and PM)
- Machine Learning epidemiological model to predict health policy scenarios through a what-if approach
Front-End (FE)
Graphical user interfaces represented by a web platform focused on maps, the main results of which are:
- Analysis of the spread and dynamics of past outbreaks
- Monitoring of the ongoing outbreak through diffusion maps with municipal detail and census section
- Prediction of the widespread epidemic and the effectiveness of blocking/mobility limitations to curb the epidemic in the study area
- Reporting map and historical series of health parameters and indicators
EPICO19 has authenticated access for public health experts with all the features and public access for citizens who can consult maps and graphics decided by the AUSL.
-
© Copyright TerrAria s.r.l. – via Melchiorre Gioia, 132 20125 Milano – Italia | info@terraria.com | Tel. 02 8708 5650 | Privacy e Cookie Policy
